4.4.2.1 Complying with the Golden Rule
Complying with the Golden Rule is the most important behavioural requirement for interactions between people living in the same society.
There is commonality in what people regard as acceptable behaviour, despite their different beliefs and religions. John Rawls refer to people having different “comprehensive moral conceptions” in his book Political Liberalism.[1] As seen previously, the Golden Rule is consistent with all religions (4.2.2.2) and most philosophies (4.2.3), so it can form the nucleus of the “social” aspect of what Rawls referred to as an “overlapping consensus” on how to behave, as illustrated:
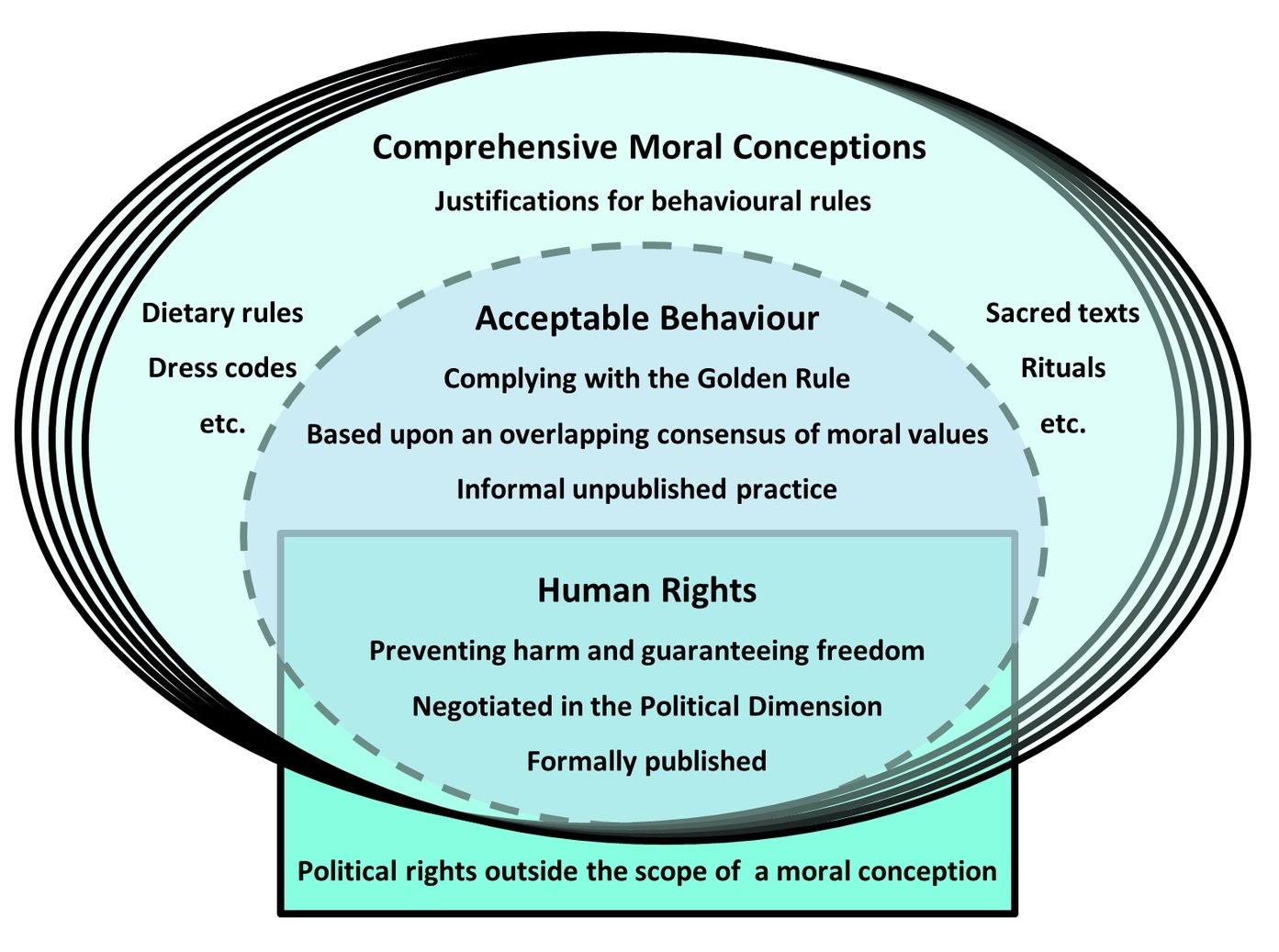
This diagram illustrates that many “comprehensive moral conceptions”, such as
religions, can be compatible with a consensus on one standard of socially acceptable
behaviour – which includes the Golden Rule and many, but not all, agreed human
rights. Many aspects of religion do not affect people’s behaviour towards
others.
Complying with the Golden Rule is at the heart of this concept of acceptable behaviour: avoid doing to others what you don't want done to you. It only requires tolerance. Sympathy is not required or assumed. It is sufficient to prevent friction and violence, even where people don’t want to have much interaction with members of other communities – though people may have higher expectations from those they know well, as described earlier (4.3.2).
(This is an archive of a page intended to form part of Edition 4 of the Patterns of Power series of books. The latest versions are at book contents).